Category: Bookkeeping
- Bookkeeping
- By grevion2022
Construction Company Bookkeeping For Contractors All Across The USA Including Alaska And Hawaii Seattle
Content
It offers a wide array of services, including bank reconciliations, consultations, general ledger maintenance, and payroll processing and reporting. Moreover, the company also offers a business owners package, which is a four-part client care system that includes initial strategy sessions, proactive monitoring, tax planning, and tax preparation. Yuriy Akopyan, the founder, has over 20 years of experience in the accounting bookkeeping services seattle industry. Your Balance Sheet, LLC is an Everett business that has been serving the Greater Puget Sound area for over 18 years. The business offers a free consultation, and services include bookkeeping clean-ups, tax filing, daily accounting, audit support, accounting leadership, software conversions, and monthly financial statements. Your Balance Sheet, LLC is accredited by the Better Business Bureau and has an A+ rating.
- It provides personal financial advice in dealing with financing children’s education, purchasing a home, preparing for retirement, and planning an estate.
- Your Balance Sheet, LLC is accredited by the Better Business Bureau and has an A+ rating.
- I strive to work in the most efficient manner possible so that my clients receive what they need, when they need it.
- Cheryl’s personable attention and wide experience in the Seattle area in accounting will be a strong asset to your Seattle business.
- BooXkeeping is a nationwide provider of affordable outsourced bookkeeping services to small and medium-sized businesses.
- Safstrom & Company has operated for nearly five decades, offering professional accounting services to the Seattle area.
Linda M. Teachout, CPA, PLLC is accredited by the Better Business Bureau and has an A+ rating. System Six Bookkeeping, LLC is a Seattle business that provides bookkeeping and https://www.bookstime.com/articles/remote-bookkeeping accounting services for small businesses. Services include monthly financial reporting, payroll, data entry, local and state tax filing, and accounts receivable and payable.
To Growing Small Businesses
The Hagen Firm promises professional service, and an approachable, friendly staff. Sprute & Davis provides professional accounting and consulting services to Seattle and the surrounding area. The company boasts over three decades of experience, and this qualified firm provides a variety of services to businesses, non-profits, estates, trusts, and individuals. These services include tax planning and prep, businesses consulting, financial reporting, software support, bookkeeping, and payroll help.
Our Seattle CPA firm offers accounting, tax, consulting and advisory services tailored to meet the individual needs of each client. Over the years we have worked with many Seattle area businesses and individuals. Ledger Pros is a Seattle business that provides bookkeeping services and has over 70 years of combined experience. Services are payroll, profit and loss statements, purchase and receipt maintenance, tax reporting, and other account services. Ledger Pros is accredited by the Better Business Bureau, is a FreshBooks Cloud Accounting Certified Accountant, and is Bill.com Certified.
What do CPAs do?
Eastham Foster is a member of the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants and the Washington State Society of Certified Public Accountants. Newman Dierst Hales is a Seattle tax and accounting firm that has been serving businesses and individuals for over nine years. Partners Nolan A. Newman, CPA and Ann M. Imus, CPA have over 64 years of combined experience. Akopyan & Company, CPA, is an accounting firm that serves clients in Seattle and the nearby areas.
Bookkeeping services include income statement, general ledger maintenance, income statements, and checks and balances. Honest Buck Accounting offers an initial consultation and has three packages. MAS Certified Public Accountants is a Seattle business that has been serving individuals and businesses for over nine years. Areas of practice include bookkeeping, tax planning, payroll, accounting software, cash management, entity selection, and advisory.
Company
However, this doesn’t necessarily mean they will be the best candidate to provide the help you need with your income tax preparation. The IRS explains that CPAs, attorneys and enrolled agents are all allowed to legally represent their clients before the IRS. They have a more thorough understanding of tax code than an individual operating solely with a PTIN or an Annual Filing Season Program participant who provides their services on a volunteer basis.
- See more reviews, compare prices, and hire your favorite pros all with Thumbtack.
- As an experienced Seattle, WA CPA firm, we’re able to offer a wide range of industry-specific accounting and bookkeeping solutions to businesses in a variety of niche industries.
- Once we have everything set up, we’ll complete a month of your bookkeeping in 1-2 days.
- Shortly after you sign up, we’ll give you a call to learn more about your business and bookkeeping needs.
- Seattle based businesses are able to take advantage of Washington State’s no corporate tax and personal income tax laws.
- We also provide bookkeeping data analysis to help you make more informed decisions about your business finances.
The woman-led team of accountants and tax advisers works with businesses and tailors support packages that reflect their industry-specific needs. The company networks with other industries, such as website designers, marketers, and insurance agents to help keep startups running. Linda M. Teachout, CPA, PLLC is a Shoreline business that has been serving individuals and businesses in the Greater Puget Sound area for over five years.
Check out the average hourly rate for accounting services in your area. BooXkeeping is a nationwide provider of affordable outsourced bookkeeping services to small and medium-sized businesses. Businesses in Washington State and Seattle do not pay a corporate or personal income tax. However, there are still some taxes that some businesses may be subject to such as the business and occupation tax (B&O), retail sales tax, and property taxes. BooXkeeping will make running your business smoother than ever with our team of U.S.-based experts handling day-to-day bookkeeping tasks and integrating seamlessly into your existing accounting software.
The firm was founded nearly seven decades ago, giving it a rich history. Clients praise Minar Northey’s ability to make financials as stress-free and easy as possible. Alisa NA, CPA, is an accounting firm that has been providing accounting services since 1995 to its individual and business clients in Seattle. It provides personal financial advice in dealing with financing children’s education, purchasing a home, preparing for retirement, and planning an estate. It also offers corporate new business setup and consultation, accounting and bookkeeping, financial statement preparation, payroll, tax planning, and tax filing services to business clients. It also caters to corporate, partnership, and personal income tax services.
Your Board of Advisors and especially your banker will be unhappy; however, they may not say it outright, just that your loans, lines of credit and referral opportunities may be limited. When you choose BooXkeeping, you can rest assured knowing that you’re getting the most reliable bookkeeping services from a team “obsessed” with helping your business. Your bookkeeping team consists of 3 professionally trained bookkeepers, including one senior bookkeeper who reviews all of your monthly statements and your Year End Financial package. Get your bookkeeping, income tax prep, and filing done by experts—backed by one powerful platform. We guarantee accuracy for bookkeeping and ensure that all records are up-to-date. Our bookkeepers make sure to double check all financial records and calculations to ensure accuracy.
Shortly after you sign up, we’ll give you a call to learn more about your business and bookkeeping needs. On this call, we’ll connect your accounts to Bench, and gather any extra documentation we need to complete your books. As your financial advocate, Vazquez CPA & Company can provide the financial advice and accounting support to help you get to the next level. At My Seattle Bookkeeper you will be guaranteed to receive efficient, honest bookkeeping service that will ensure your satisfaction and ongoing business. At My Seattle Bookkeeper, we provide personalized small business bookkeeping that you can rely upon. All your monthly bookkeeping tasks are handled for a low fixed monthly rate with no long-term contracts.
Service Providers
We’re a virtual firm of accountants who help small business owners and freelancers nail down their income & expenses, rectify historical books & setup long term business goals to achieve your vision for success. Our Seattle bookkeepers work exclusively with QuickBooks for a seamless integration into our client’s current process. We can help you set up your company accounts, review bookkeeping data and generate reports. This allows you to make more informed decisions in a timely manner, saving you time and money. Vazquez & Co. is a Seattle CPA firm that has been serving small businesses for over 19 years. The business offers a free consultation, and services are outsourced bookkeeping, outsourced accounting, payroll services, and outsourced CFO and controller.
- Bookkeeping
- By grevion2022
Guide to projecting cash flow forecasts + examples
Content

Putting aside some extra cash as a buffer is especially useful for those building their first projections, just in case they accidentally leave something out. Furthermore, if you provide customers with a 30-day payment schedule and a majority pay on the last possible day, make sure that cycle is accurately reflected in your projection. Understanding and predicting the flow of money in and out of your business, however, can help entrepreneurs make smarter decisions, plan ahead, and ultimately avoid an unnecessary cash flow crisis.
Essentially adding all the cash inflows and deducting the cash outflows, result in your cash position over a period of time. Direct forecasting is typically a highly accurate outcome because the time horizon is short-term, and the calculations are based on actual cash flows. However, in the long term, it becomes increasingly difficult to predict this data. The result of direct forecasting provides you with a good picture of your company’s working capital. A cash flow projection is a forecast of a company’s expected cash inflows and outflows. The projections are typically made for a specific period of time, such as a month, quarter, or year.
Cash Flow Projection Definition
Cash flow forecasts help you anticipate potential revenue shortfalls and surpluses by predicting when money will enter or leave your accounts. The output section contains all the important figures we would like to get out of a cash flow forecast model. While all these benefits won’t come all at once, entrepreneurs can use their cash flow projection to become better operators and better decision makers with each passing month. Those who want to be extra cautious with their projections can even include an “other expenses” category that designates a certain percentage of revenues for unanticipated costs.
What is the cash flow formula?
The formula for operating cash flow is: Operating cash flow = operating income + non-cash expenses – taxes + changes in working capital The restaurant's operating cash flow therefore equals $20,000 + $1,500 – $4,000 – $6,000, giving it a positive operating cash flow of $11,500.
Appointing a specific group to put a standard system in place for cash flow forecasting will ensure future accuracy. A common challenge to accurate cash flow forecasting is the https://www.bookstime.com/ lack of a standard system or methodology used throughout the organization. Inaccurate cash flow forecasts are often the result of poor communication between business segments.
Step 4: Enter your estimations into your cash flow forecast
Keep in mind that the longer the time horizon to forecast, the less accurate it is expected to be. Cash flow forecasts also allow you to predict which months will see strong positive cash flow and plan how to https://www.bookstime.com/articles/cash-flow-forecast effectively use this excess cash. Predict which months might see a cash deficiency – whether that be from poor predicted sales, after a potential investment, or implementing a planned new product or service.
- Once you’re in the habit of creating cash flow projections, it becomes easier to improve their accuracy over time.
- The projections are typically made for a specific period of time, such as a month, quarter, or year.
- Inaccurate cash flow forecasts are often the result of poor communication between business segments.
- Your forecast will clearly highlight the issue of overdue payments, in turn allowing you to identify the late-paying clients.
- In particular, get clear on how long it takes for you to receive payment from customers and when your bill payments are typically due.
- To increase the accuracy of your forecasts, you need to analyze as much data as possible.
The forecast is rolled forward every time there is a month of historical data to input. Rolling forecasts work best when key cash flow drivers are modeled explicitly and directly drive forecast cash flow inputs. We’ll look at the structure of a robust and flexible monthly cash flow forecast model for a retail store business in the following sections. You may also consider adding the opening and closing balance of your bank account to your cash flow forecast.
Sales income
We suggest using the direct method to gain quick foresight into your short-term future financial standings. In 2018, a CB Insights study that analyzed 101 startup failures revealed that running out of cash was the second most common cause of business failure — about 29 percent of businesses failed for that reason. Since it is based on the historical data, the more data you provide, the higher the accuracy is. However, you should not entirely rely on FORECAST function since it cannot consider factors not viewable in the historical data.

Short-term cash flow forecasting might look at a period of 30 days (or even several weeks), while longer-term forecasting will look at a quarter, a year, or even multiple years. Certain industries are more cash intensive than others and require a good understanding of what the cash balance will be at any given time. You can utilize the same budget you might use for a monthly, or even quarterly, cash flow forecast simply by identifying the days that fixed costs get paid. There are several challenges that finance and treasury teams face related to cash flow forecasting. These are important to understand and should be tackled by businesses in order to efficiently produce accurate cash flow forecasts.
Cash Flow Projection: Statements & Example
For granular short-term forecasts on a daily basis, as in the example below, we consider all outflows and inflows, the net cash flow, and the closing balance for each day. When done accurately cash forecasting helps businesses predict their future financials. It can help with identifying potential cash surpluses or shortages and that information is essential for making informed strategic decisions. Cash flow forecasting is a cash projection process to estimate the financial position of a business over a specific period of time. It is measured by comparing the cash in- and outflows of the business in the future.

This information can be crucial in budget planning and forecasting for the upcoming year. A good cash flow forecast will show you exactly when cash might run low in the future so you can prepare. It’s always better to plan ahead so you can set up a line of credit or secure additional investment so your business can survive periods of negative cash flow.
Cash flow statements
Look for ways to improve the data collection and forecasting processes—with software, for example—to help ensure greater accuracy for your future projections. The further into the future a forecast looks, the less accurate it will be. In addition to having less data to rely on, long-term forecasts are open to unexpected changes that can drastically change your predictions. So when you push your forecast further out, expect the data to change over time as well. For instance, consider a service-based business with Net-30 payment terms. On paper, everything may look great because there’s a healthy flow of money coming in from work performed.
What is a typical cash flow statement?
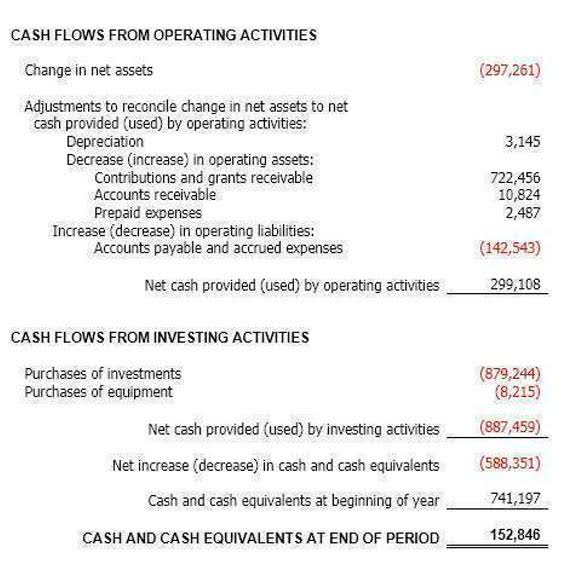
A typical cash flow statement comprises three sections: cash flow from operating activities, cash flow from investing activities, and cash flow from financing activities.
The purpose of a cash flow projection is to give business owners and managers a better understanding of the company’s financial situation. It can help them make decisions about how to allocate resources and manage risks. Cash flow projections show the amount of cash on hand at the beginning and at the end of each month.
- Bookkeeping
- By grevion2022
Chart of Accounts: Definition and Examples
Content
One of these statements is the balance sheet, which lists a company’s assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity. The company may look like a very profitable business, but that isn’t really true because three years-worth of revenues were combined. In order to properly compute for the year’s total profits, as well as the total expenses, the temporary accounts must be closed, and a new balance created at the beginning of a new accounting period. Small businesses might record hundreds or thousands of transactions each year. These main accounts help organize transactions into coherent groups that you can use to analyze your business’s financial position.
For these reasons, it is important to have a team or accounts payable system that is up-to-date and well-run to ensure that your organization is not missing out on opportunities or reporting inaccurate financials. Should any of the goods or services listed above be purchased on credit by your organization, it is important to immediately record the amount to AP. This will ensure your balance sheet is kept up-to-date and accurately reports on the total amount owed to your vendors, enabling transparency in your book keeping efforts and accounting process. When you have a system to manage your working capital, you can stay ahead of issues like these. Calculating your business’s accounts receivable turnover ratio is one of the best ways to keep track of late payments and make sure they aren’t getting out of hand.
What is a chart of accounts?
When these transactions generate income, they are transferred to another part of the balance of payments. If they produce investment income, they are transferred to the financial account. If they produce income from goods or services, they are transferred to the current account.
A temporary account is an account that is closed at the end of every accounting period and starts a new period with a zero balance. The accounts are closed to prevent their balances from being mixed with the balances of the next accounting period. The objective is to show the profits that were generated and the accounting activity of individual periods. The quick ratio (also known as the Acid test ratio) is a type of liquidity ratio used to assess the ability of a company to meet its short-term liabilities using the most liquid assets. It is a ratio that compares how the short-term assets of a company can be used to pay for short-term liabilities. This is another type of financial leverage ratio that indicates how a company finances its operations, whether through debt or through current revenues or shareholders.
What are real accounts?
Simply it is an account to organize the transactions related to natural and artificial persons. A chart of accounts provides a listing of all financial accounts used by particular business, organization, or government agency. The accounting period started on January 1 and it will end on December 31.
Important to know about Real Accounts – In spite of the fact that “debtors” are assets for the company, they continue to be classified as personal accounts. This is because ‘debtors’ belong to individuals or entities https://simple-accounting.org/real-accounts-vs-nominal-accounts-definition/ and personal accounts specifically serve the purpose of calculating balances due to or due from such 3rd parties. In accounting, you deal with a variety of accounts to balance and organize your books.
Working capital
Real accounts reflect the current and ongoing financial status of a company because they carry their balance forward into the next accounting period. These accounts are typically reported on the balance sheet at the end of the year as assets, liabilities, or equity. A real (permanent) account is an account that retains its balance permanently. Balance sheet accounts are permanent, and income statement accounts are temporary.
What is an example of real account transaction?
The ledger accounts which contain transactions related to the assets or liabilities of the business are called Real accounts. Accounts of both tangible and intangible nature fall under this category of accounts, i.e. Machinery, Buildings, Goodwill, Patent rights, etc.
This is an important limitation of the balance sheet that any lender needs to take note of it. The dividends payable are the unissued dividends that are authorized but https://simple-accounting.org/ are not issued yet. For a company that pays dividends, you can check the amount to be paid as dividends under the dividend payable account in the liability section.
- Bookkeeping
- By grevion2022
Capital Budgeting Importance Importance with Explanation
Content
The Payback Period analysis does not take into account the time value of money. To correct for this deficiency, the Discounted Payback Period method was created. As shown in Figure 1, this method discounts the future cash flows back to their present value so the investment and the stream of cash flows can be compared at the same time period. Each of the cash flows is discounted over the number of years from the time of the cash flow payment to the time of the original investment. For example, the first cash flow is discounted over one year and the fifth cash flow is discounted over five years. Project B has the next shortest Payback (almost three years) and Project A has the longest (four years).
- Payback analysis is usually used when companies have only a limited amount of funds (or liquidity) to invest in a project, and therefore need to know how quickly they can get back their investment.
- For a comparison of the six capital budgeting methods, two capital investments projects are presented in Table 8 for analysis.
- Again, 27% firms always used IRR, but interestingly all the respondents firms use IRR with NPV as a secondary method.
- Typically, businesses should pursue every project and opportunity which improves shareholder value.
- With project investments below pre-COVID levels, selecting the right projects and assets to invest in is critical.
- If the NPV is less than zero, the rate of return from the investment is less than the required rate of return.
Most times, a company evaluates the lifetime cash inflows and outflows of a prospective project to ascertain if the potential returns gotten meet the desired target benchmark, also referred to as “investment appraisal.” You’d use the process of capital budgeting to make a strategic decision whether to accept or reject a proposed investment project. Effective capital budgeting is almost impossible without a capital budgeting platform that integrates with other key project management and PPM areas.
Why Is the Internal Rate of Return Important to an Organization?
Thus, the discounted payback period could be defined as the number of periods it takes for the cumulative discounted cash flow to become equal to the initial outlay. Internal rate of return (or IRR) is defined as the discount rate, which makes the present value of all projected cash inflows equal to the initial cash outflow. The principles of capital budgeting have been adapted for many corporate decisions, including working https://investrecords.com/the-importance-of-accurate-bookkeeping-for-law-firms-a-comprehensive-guide/ capital management, leasing, mergers & acquisitions (or M&A), bond refunding, and investment decisions. Second, it only considers the cash inflows until the investment cash outflows are recovered; cash inflows after the payback period are not part of the analysis. However, if a long-term investment carries higher than average risk for the firm, the firm will use a required rate of return higher than the cost of capital.
A capital budget can also assist with securing additional financing from banks or investors when pursuing a new investment project. The process of capital budgeting ensures that decision-making at your enterprise is thoughtful and data-centered. It relies on teams coming together to compare top project ideas before analyzing which best align with the company’s needs. This attention to detail ensures that capital spending decisions align with the organization’s overall business strategy. Capital budgeting is a useful tool that companies can use to decide whether to devote capital to a particular new project or investment. There are several capital budgeting methods that managers can use, ranging from the crude but quick to the more complex and sophisticated.
Constraint Analysis
For this reason, capital expenditure decisions must be anticipated in advance and integrated into the master budget. The plans of a business to modernize or apply long-term investments will influence the cash budget in the current year. Capital budgeting is concerned with identifying the capital investment requirements of the business (e.g., acquisition of machinery or buildings). In a separate part of this chapter, recent budgets have presented alternative
capital budgets that offer two alternative definitions emphasizing different
purposes. One definition emphasizes the provision of government services
to the public. A second definition emphasizes investment in capital that
contributes more directly to the economic growth of the nation.
- State and local capital budgets include some subset of physical capital
owned by the state or locality and, in certain cases, state grants to localities
to buy physical capital. - So only the discounting from the time of the cash flow to the present time is relevant.
- In Table 3, a Discounted Payback Period analysis is shown using the same three projects outlined in Table 1, except the cash flows are now discounted.
- Capital budgeting’s main goal is to identify projects that produce cash flows that exceed the cost of the project for a company.
A sound capital budgeting decision is very critical for a firm because it is aligned with the firm’s primary objective (wealth maximization), and it requires a substantial amount of resource and long-term commitment. Once the decision has been made, the process cannot be manipulated without incurring losses (Hall and Millard, 2010). Capital budgeting is a major terrain of the sphere Navigating Law Firm Bookkeeping: Exploring Industry-Specific Insights of financial management. Gitman et al. (2015) define capital budgeting as “the process of evaluating and selecting long term investment consistent with the firm owners’ goal of wealth maximization” (p. 344). Universally accepted definition yet to exist, because it is involved with multifaceted activities and influenced by many changing factors in the organizational environment.
- Bookkeeping
- By grevion2022
What Are Long-Term Liabilities?
Content
If a company can comfortably pay its liabilities, it’s in good financial shape and could potentially be a good investment. Companies list liabilities on their balance sheet after bookkeeping for startups listing their assets. When the total value of a company’s liabilities is greater than the total value of its assets, the company is considered to be financially insolvent.
Bonds are shares in a company’s debt, although they can also be issued by local and national governments. The issuer promises to pay interest every six months and pay the principal or maturity at a specified future date. Notes payable are functionally the same as bonds, although they have a shorter maturity period.
IAS plus
In a small business owned by one person or a group of people, the owner’s equity is shown in a Capital account. In a larger business that’s incorporated, owner’s equity is shown in shares of stock. Capital (CAP) – A financial asset and its value, such as cash or goods.
What are 3 examples of liabilities?
- Bank debt.
- Mortgage debt.
- Money owed to suppliers (accounts payable)
- Wages owed.
- Taxes owed.
In our next post, we look at some ideas to engage with and manage longer-term creditors. Welcome to the fourth piece in our ‘Building a resilient balance sheet for 2021’ series looking at solutions and opportunities for 2021 viewed through the balance sheet. As you can see, assets and liabilities look similar in most business situations.
The Importance of Long Term Liabilities
A long-term liability is defined as financial obligations of a business that are not due for more than a year. Businesses should ensure that they have reasonable forecasting models in place so that any potential changes in financial markets or other external factors can be anticipated. By monitoring long-term liabilities regularly, businesses can reduce risk and create value for shareholders’ equity over the long haul.
This means that the holder is now earning finance income in two different ways. Secondly, they are earning another $1m over three years in the form of receiving more money back than they invested. Changes to a company’s share capital such as the introduction of preference shares may require changes to the articles of association.
Balance sheet – Key takeaways
This time delay between when your business pays money out (e.g. to suppliers) and when it receives money back (e.g. from sales) is known as the working capital or operating cycle. The working capital requirement of your business is the money you need to cover this time delay. Liabilities – All the debts the company owes, such as bonds, loans, and unpaid bills.
Accrued Payroll
This represents the amount earned by Fred’s employees, but which has not yet been paid to them. This is because employees are paid in arrears for time they have already worked. Every organization has some amount of money owed to its employees but not yet paid. By planning your business’s finances carefully and avoiding reckless spending, you can stay on top of your liabilities and run an effective, profitable business. Pension liabilities refer to the responsibility of an employer to make regular payments for the pensions of their retired or former employees. Bonds payable are bonds issued by companies or other organisations in order to raise funds for various purposes.
Relax about tax
If you have taken out a business loan with a five-year repayment term, this will be classed a non-current liability. Another key Equity account is Retained Earnings, which tracks all company profits that have been reinvested in the company rather than paid out to the company’s owners. Small businesses track money paid out to owners in a Drawing account, whereas incorporated businesses dole out money to owners by paying dividends. Expenses (Fixed, Variable, Accrued, Operation) (FE, VE, AE, OE) – The fixed, variable, accrued or day-to-day costs that a business may incur through its operations. Examples of expenses include payments to banks, suppliers, employees or equipment.
Working capital is calculated by taking your current assets subtracted from current liabilities. Because non-current assets are longer-term investments, you’ll always factor depreciation into the balance sheet. It looks at every asset, liability and shareholder equity at a specific point in time. An income – or profit & loss – statement focuses on what you’ve bought and spent over a certain period of time. Under assets, you’ll record everything your business owns, from cash in the bank to equipment and property (more detail on this below). It shows your business’s net worth and overall financial health, by recording your assets, liabilities and shareholder’s or owner’s equity.
What are contingent liabilities?
As noted earlier, the effective interest rate will be given to candidates in the exam. The principles of amortised cost accounting mean that interest must be recorded on the amount outstanding. For example, on a $10m 5% loan, with $10m repayable at the end of a three-year term, interest would simply be recorded as $500,000 a year. It is always a good idea to check on the effects of any investment in fixed assets on forecast liquidity and cash flow before entering into any commitment. Accounts payable (AP) refers to money that the company owes to its suppliers or vendors for goods or services that have been purchased on credit. Accounts payable are typically paid within days, depending on the terms of the credit agreement.
- Having high current assets is typically considered “safe”, as you should be able to get your hands on plenty of cash quickly if you need to.
- It makes the purchase using a bank loan facility to pay off the new asset over 12 months.
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) – The direct expense related to producing the goods sold by a company.
- It’s useful to know what the ratio is because, on paper, two companies with very different assets and liabilities could look identical if you relied on their working capital figures alone.
- ___ are what the company owes to creditors and banks, such as bank loans or unpaid bills.
- First, it includes the amount funded by the owners or shareholders of a company for the initial start-up of the business.
- Bookkeeping
- By grevion2022
Depreciation Expense vs Accumulated Depreciation: What’s the Difference?
Content
- Example of Accumulated Depreciation on a Balance Sheet
- What is the fundamental calculation method for Accumulated Depreciation?
- Understanding Accumulated Depreciation
- Differences − Accumulated Depreciation and Depreciation Expense
- Accounting Entry to Amortize Intangible Assets
- Accumulated Depreciation
This expenditure arises independently of the worth of the firm’s assets. As a result of this, it is vital to create a distinction between cumulative depreciation and the spending of depreciation. Depreciation expense is the periodic depreciation charge that a business takes against its assets in each reporting period. The intent of this charge is to gradually reduce the carrying amount of fixed assets as their value is consumed over time.
What are the different types of depreciation expense?
- Straight Line.
- Declining Balance.
- Double Declining Balance.
- Sum of the Years' Digits.
- Units of Production.
This value is what the asset is worth at the end of its useful life and what it could be sold for when the company has finished with it. Depreciation expense is the amount of depreciation that is reported on the income statement. In other words, it is the amount of an asset’s cost that has been allocated and reported as an expense for the period (year, month, etc.) shown in the income statement’s heading.
Example of Accumulated Depreciation on a Balance Sheet
An asset’s depreciation expense is the sum of its allocated and reported costs at the end of each reporting period. It is calculated by subtracting the value an asset is predicted to retain until it is exhausted from the asset’s worth at the time it was acquired. Then, you need to divide that sum by the expected lifespan of the asset. It is reflected in the income statement and helps a corporation save money on taxes by decreasing its taxable income. Accumulated depreciation represents the total depreciation of a company’s fixed assets at a specific point in time. Also, fixed assets are recorded on the balance sheet, and since accumulated depreciation affects a fixed asset’s value, it, too, is recorded on the balance sheet.
- Depreciation expense is recognized on the income statement as a non-cash expense that reduces the company’s net income or profit.
- When this amount is deducted from an asset’s initial purchase price, the resultant balance on the balance sheet is negative.
- As a contra-asset account, accumulated depreciation is deducted from the asset’s cost on the balance sheet to determine the asset’s book value.
- Also, we might state that book value and accumulated depreciation are significant accounting ideas connected to the depreciation of fixed assets.
- The total amount of depreciation expense that has been recorded on a fixed asset over the course of its useful life is known as accumulated depreciation.
Accumulated depreciation is documented in a counter-asset account, which has a credit balance and reduces the fixed asset’s gross value. Accumulated depreciation is the cumulative amount of depreciation that has piled up since the initiation of depreciation for each asset. This information is stored in a contra asset account, which effectively reduces the balance of the fixed asset account with which it is paired. Depreciation expense is not a current asset; it is reported on the income statement along with other normal business expenses. Accumulated depreciation is a running total of depreciation expense for an asset that is recorded on the balance sheet.
What is the fundamental calculation method for Accumulated Depreciation?
Also, we might state that book value and accumulated depreciation are significant accounting ideas connected to the depreciation of fixed assets. While book value refers to the asset’s reported value on a company’s balance sheet, accumulated depreciation indicates the total amount of depreciation expense recorded on an asset during its useful life. For proper financial reporting, determining a company’s financial status, and for tax purposes, it’s crucial to comprehend these ideas. The accumulated depreciation account is a contra asset account on a company’s balance sheet. It appears as a reduction from the gross amount of fixed assets reported. Accumulated depreciation specifies the total amount of an asset’s wear to date in the asset’s useful life.
If the asset is used for production, the expense is listed in the operating expenses area of the income statement. This amount reflects a portion of the acquisition cost of the asset for production purposes. Now, we calculate the accumulated depreciation, which is equal to the total depreciation expense that has accrued since the asset has been in use. Therefore, a total of $16,000 in accumulated depreciation would accrue after five years. An asset’s book value is the original cost less the total amount of depreciation. As a result, the asset’s book value declines as accumulated depreciation rises.
Understanding Accumulated Depreciation
It is calculated by summing up the depreciation expense amounts for each year. Depreciation expense is considered a non-cash expense because the recurring monthly depreciation entry does not involve a cash transaction. Because of this, the statement of cash flows prepared under the indirect method adds the depreciation expense back to calculate cash flow from operations. The methods used to calculate depreciation include straight line, declining balance, sum-of-the-years’ digits, and units of production. Accumulated depreciation is usually not listed separately on the balance sheet, where long-term assets are shown at their carrying value, net of accumulated depreciation. Since this information is not available, it can be hard to analyze the amount of accumulated depreciation attached to a company’s assets.
Subsequent years’ expenses will change as the figure for the remaining lifespan changes. So, depreciation expense would decline to $5,600 in the second year (14/120) x ($50,000 – $2,000). If an asset is sold or disposed of, the asset’s accumulated depreciation is removed from the balance sheet. Net book value isn’t necessarily reflective of the market value of an asset. Depreciation expense is the amount that a company’s assets are depreciated for a single period (e.g,, quarter or the year). Accumulated depreciation, on the other hand, is the total amount that a company has depreciated its assets to date.
As a result, an asset’s book value decreases over time as it ages, representing the value loss brought on by usage, damage from use, and obsolescence. Quest Adventure Gear buys an automated industrial sewing machine for $60,000, which it expects to operate for the next five years. Based on the 60-month useful life of the machine, Quest will charge $12,000 of this cost to depreciation expense in each of the next five years. The four methods allowed by generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) are the aforementioned straight-line, declining balance, sum-of-the-years’ digits (SYD), and units of production. Put another way, accumulated depreciation is the total amount of an asset’s cost that has been allocated as depreciation expense since the asset was put into use. The total value of all the assets of a company is listed on the balance sheet rather than showing the value of each individual asset.
The account Accumulated Depreciation is a contra asset account because it will have a credit balance. The credit balance is reported in the property, plant and equipment section of the balance sheet and it reduces the cost of the assets to their carrying value or book value. Depreciation expense and accumulated depreciation are two concepts that are crucial to accounting and finance. The relationship between these two ideas is crucial for correctly reporting an asset’s value on the balance sheet and calculating a company’s net income and worth. Any accountant, financial analyst, or business owner who wants to make wise financial decisions must understand the relationship between accumulated depreciation and depreciation expense.
Keeping track of depreciation costs is essential for reporting since depreciation spreads an asset’s cost across its lifetime. Accumulated depreciation is used to calculate https://accounting-services.net/accumulated-depreciation-and-depreciation-expense/ an asset’s net book value, which is the value of an asset carried on the balance sheet. The formula for net book value is cost an asset minus accumulated depreciation.
- Accumulated depreciation is the total amount of depreciation of a company’s assets, while depreciation expense is the amount that has been depreciated for a single period.
- Again, it is important for investors to pay close attention to ensure that management is not boosting book value behind the scenes through depreciation-calculating tactics.
- Let’s say you have a car used in your business that has a value of $25,000.
- One can simply compute the depreciation expense after dividing the “asset’s cost minus its salvage value” by the asset’s useful life.
- Depreciation expense is considered a non-cash expense because the recurring monthly depreciation entry does not involve a cash transaction.
- Bookkeeping
- By grevion2022
Accounting Principles first chapter 1 Quiz Survey
Ideally, you should be able to answer those accounting questions with ease. If you can’t, you may want to get some more accounting practice. If you are unable to solve these fill-in-the-blank questions, read “accounting principles and concepts” chapter from explanations section of our website. Take this short quiz to assess your knowledge of basic accounting. The 35 questions include many topics covered in a typical Accounting 101 class. When making decisions in accounting, it is essential to consider all relevant factors.
Try out these quiz questions and answers and check your financial knowledge. Accounting principles are the common rules and guidelines that companies need to follow while preparing and presenting financial statements. Preparation is the key to success when trying to pass your accounting class. The best way to prepare for your next accounting test or quiz is to work on accounting problems you’re likely to see on your test. This free accounting principles practice test assesses your knowledge of some of the most common questions that students encounter on their accounting exams.
Financial Reporting Standards is the: IASB
Accounting is a challenging field that requires years of initial education, experience and continuing professional education. Indirect cost rate calculations can be determined https://turbo-tax.org/tax-dates-and-deadlines-in-2021/ by dividing an indirect cost by a cost object, such as sales revenues or square footage. Revenues are the sales of products or services to customers by a business.
It will help you quickly identify your strengths and focus your efforts on where you need more study and practice. There’s no need to feel confused about these basic accounting principles or stressed out because there’s never enough time to finish all the questions on your accounting quizzes and tests. My students efficiently solve accounting problems with confidence in the allotted time. I want to show you how to do this with my Pass Accounting Class program.
Using the above information prepare an October income statement
An accounting assessment test gauges an individual’s knowledge of basic accounting information, often used to screen potential candidates for bookkeeping and lower-level accounting jobs. This quiz and worksheet combo helps gauge your knowledge of GAAP. Terms you will need to know for the quiz include Economic Entity Assumption and Going Concern Principle.
EU antitrust regulators quiz cloud rivals on Microsoft’s request for … – Reuters.com
EU antitrust regulators quiz cloud rivals on Microsoft’s request for ….
Posted: Fri, 19 May 2023 07:00:00 GMT [source]
This Accounting Test is designed to help you assess your knowledge of essential accounting principles and basic concepts. This is also a useful resource for employers to examine the technical knowledge of the candidates during an accounting or finance interview. In accounting, decision-making is the process of choosing between two or more courses of action to achieve the desired outcome. Factors that should be considered when making decisions include the company’s financial position, Cash Flow, profitability, and business strategy. Accountants use the information to make decisions by analyzing data and trends to make informed decisions to help the company achieve its goals. Test your knowledge with this multiple choice question (MCQ) test on accounting principles and concepts.
Accounting
Some of the factors that may be considered include the company’s financial position, Cash Flow, profitability, and business strategy. Accounting basics include how to value business transactions, how to record activity in a company’s books and how to report business results using financial statements. Few would debate that independence in fact—that is, that the auditor is actually unbiased—is absolutely essential to the validity of an audit. Demonstrate
how to use the accounting equation to record the transaction by
completing the following sentence. Jackson would
decrease (expenses/cash/revenues) and
increase (expenses/equity/revenues) in the accounting equation. My Accounting Course is a world-class educational resource developed by experts to simplify accounting, finance, & investment analysis topics, so students and professionals can learn and propel their careers.
- It will help you quickly identify your strengths and focus your efforts on where you need more study and practice.
- NetSuite has packaged the experience gained from tens of thousands of worldwide deployments over two decades into a set of leading practices that pave a clear path to success and are proven to deliver rapid business value.
- My students efficiently solve accounting problems with confidence in the allotted time.
- This information can come from Financial Statements, internal reports, surveys, and other sources.
- There’s no need to feel confused about these basic accounting principles or stressed out because there’s never enough time to finish all the questions on your accounting quizzes and tests.
With these assessment tools, you can see how much information you’ve retained regarding the seven accounting principles discussed in the corresponding lesson. The quiz and worksheet combo will test your understanding of these principles and their purposes. Basic accounting questions focus on topics concerning the financial statements and how transactions are recorded. [Reference]Activity analysis involves studying and evaluating the activities and processes within an organization to understand their cost implications.
What is the hardest accounting standard?
IFRS 9 is probably the most complicated accounting standard ever issued, written to address the accounting weaknesses claimed to have contributed to the global financial crisis and intended to be fit for purpose for the most complex banking and financial services companies.
